DRI utilizes highly specialized imaging systems. These are necessary to meet the stringent requirements of the applications and to ensure optimal performance under an extremely broad range of often adverse conditions. But the performance demands of DRI are a moving target. They are continuously evolving due to several external factors. Some of the key drivers in this shifting landscape include:
-
Sensor Improvements
Ongoing technological advances continue to yield sensors with smaller pixels and larger pixel counts (meaning increased camera resolution). As a result, builders of IR imagers must strive to keep them from becoming "optics-limited." This refers to a condition where the performance of the imaging system is primarily constrained by the performance of the optics, rather than by the sensor.
Today, sensors with a 10 μm pixel pitch are not uncommon, and they are trending towards even smaller sizes (8 μm, 7.5 μm or even 5 μm pixels). The SXGA sensor format (1280 x 1024 pixels) is relatively standard, with some systems utilizing even full HD format (1920 x 1080 pixels) sensors.
-
SWaP-C Optimization
Size, weight, power, and cost (SWaP-C) optimization is a key imperative in military system design today, guiding the development of advanced technologies across many platforms. For DRI systems, in particular, the increasing use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones for surveillance introduces especially strict SWaP constraints. These platforms demand lightweight, compact, and energy-efficient optical systems that do not sacrifice performance.
-
Multi-Spectral Operation
Modern surveillance systems often benefit from multispectral imaging. By operating over multiple spectral bands simultaneously – including visible, SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR – they can perform more effective surveillance over a wider range of lighting and weather conditions. This enhances overall situational awareness and expands the capability for accurate detection, identification, and recognition of specific elements and threats within a scenery.
-
Environmental and Operational Challenges
Security and surveillance operations often occur in harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, rain, fog, dust, and saltwater spray. Missions are carried out both day and night. Imagers may be subjected to shock and vibration. And their external surfaces may need to be cleaned periodically. Lenses must be designed to withstand these all these environmental and operating scenarios without compromising performance.
Addressing each of these requirements requires deploying a specific technological arsenal in terms of both design and fabrication. Here, we'll review some of the methods employed at MKS Ophir to meet the rigorous demands of modern security and surveillance operations and consistently satisfy advanced DRI and SWaP-C requirements.
-
DRI Resolution Requirements
Ophir possesses a comprehensive suite of capabilities to address even the most demanding resolution and optical performance requirements for DRI lenses. The foundation of these capabilities lies in our design process. Our engineers have a wealth of experience with DRI lenses and utilize the most advanced optical design software available. This enables us to create highly innovative solutions.
A critical factor in ensuring our designers' success is that our manufacturing capabilities provide them an expansive design space. That is, their design toolbox includes an extensive array of advanced materials, surface shapes, and surface types.
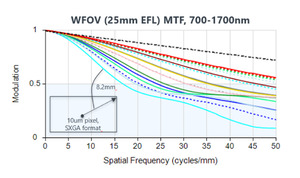
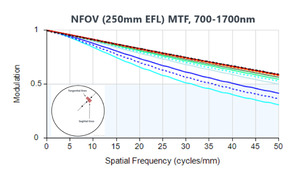
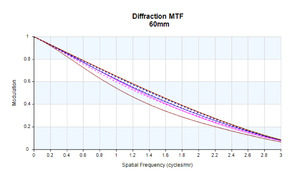
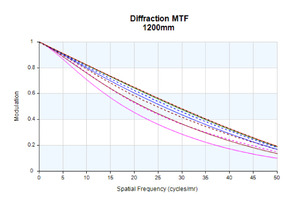
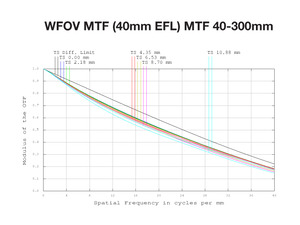
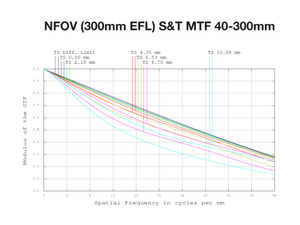
The ability to use virtually any desired surface shape or type – including traditional spheres, aspheric elements, freeforms, and even diffractive or holographic elements – enables us to achieve high MTF targets, minimize chromatic aberrations, and maintain superior performance throughout the entire zoom range of the lens.
Of course, the full performance potential of our designs can only be realized if they are faithfully reproduced in production. Our extensive range of high-precision fabrication techniques are essential in achieving this goal. This includes the ability to accurately produce optical surfaces and maintain tight mechanical tolerances on components. It also involves the ability to deposit high-quality coatings. Finally, we employ a variety of techniques to ensure that optical elements are perfectly aligned within an assembly.
It's also worth noting that Ophir can fabricate large diameter optics. These can be crucial for achieving very high magnifications in DRI zoom lenses.
Another essential advantage at Ophir is that we bring design and manufacturing together – our entire process from design through final assembly is all performed in a single facility. One example of where this helps us is in producing complex assemblies. Here, it's possible for us to use an interferometer to measure an assembly during Another essential advantage at Ophir is that we bring design and manufacturing together – our entire process from design through final assembly is all performed in a single facility. One example of where this helps us is in producing complex assemblies. Here, it's possible for us to use an interferometer to measure an assembly during production and then feed the actual test data back to the designer. They can then recalculate any changes in component spacing or alignment needed to improve performance, and these can be directly implemented
Having vertically integrated approach within a single facility also enables us to fully implement design for manufacturing (DFM) principles and derive the greatest benefits of that practice. Because our designers participate in the fabrication process, they can see which design approaches are most practical and successful. This is essential to the process of continuous improvement that enables us to successfully keep pace with the ever-increasing demands of the market.
-
SWaP-C Optimization
Leveraging a variety of advanced IR materials also allows us to minimize the total element count in a lens system, thereby decreasing package size and weight and even reducing manufacturing costs. The use of aspheres and diffractive capabilities, in particular, offers another powerful tool for minimizing lens aberrations and reducing component count.
Together, these are critical to our ability to produce continuous zoom lens designs. Being able to use a single lens instead of multiple, single focal length lenses (or even multiple zoom lenses with smaller focal length ranges) is a very powerful way to reduce system size and weight while still maintaining high performance. It also provides greater flexibility for the user by allowing rapid changes in magnification during operation.
Our capabilities for SWaP-C optimization are further extended through the use of folded-optics configurations, as well as multi-spectral designs.
-
Environmental Stability and Durability
Much of the technology used to enhance the environmental characteristics of long range DRI lenses relates to materials – both optical and mechanical. For example, materials such as titanium and magnesium alloys are often used in the construction of our lenses. These materials are specifically chosen for their combination of mechanical strength, low density (meaning light weight), and resistance to corrosion.
Athermalization techniques are employed by our engineers to ensure that the lenses maintain focus and performance across a wide range of temperatures. Combining materials having different thermal expansion coefficients enables us to create assemblies that inherently compensate for thermal changes. Lenses that remain stable and accurate in varying environmental conditions reduce the need for frequent recalibration, enhancing the operational efficiency of surveillance systems.
In terms of optics, our lenses are equipped with hard carbon (HC / DLC) and high durability (HD) coatings. These enhance resistance to scratching, abrasion, and environmental degradation. This ensures that the lenses maintain high performance even under adverse conditions and extends their operational lifetime.
Ophir lens assemblies are optimized for weight and rigidity, and to withstand shock and vibration. Our engineers design and test any moving parts (like zoom mechanisms) to guarantee long life without maintenance in extreme environmental conditions. Ophir lenses meet or exceed IP67 environmental standards, providing reliable performance in rain, dust, and other harsh environments.
-
Production Capabilities
Ophir manufactures a wide range of optics for security and surveillance applications, including:
- SWIR lenses
- MWIR lenses for cooled cameras
- LWIR lenses for uncooled cameras
- Lightweight IR zoom lenses
- Long-range IR zoom lenses
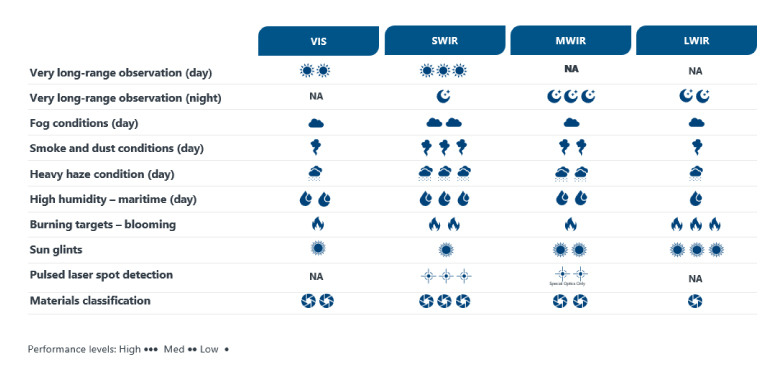
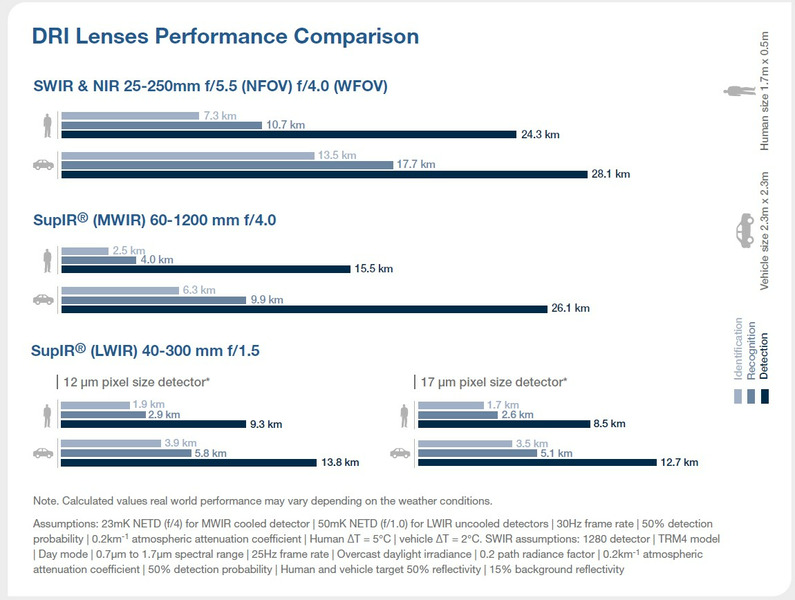
We offer lenses for different spectral ranges because there is no single spectral region that can provide the "best" results for every operational parameter in every application. The chart summarizes where each type of long-range DRI lenses excels, as well as its drawbacks.






 Ultra-High Velocity
Ultra-High Velocity